Have Jenkins Tag your Releases
17 Oct 2016In this post I’ll describe a short script to help Jenkins make git tags and push them to your repository.
This technique pairs really well with a previous post titled Automating Release Management with Gradle and Jenkins.
Configure your build to write out the build version
This step is a little tricky, as it depends on the shape of our project and the plugins you use to build it.
Here’s the context:
- Something has just finished running your build.
- Some step in the build wrote the build version to a file in the build result.
There are a lot of ways to do the latter with Gradle. An simple example would be to include this configuration for the jar (or war) Task:
jar {
manifest {
attributes(
'Implementation-Title': project.name,
'Implementation-Version': project.version
)
}
}
Alternatively, if you are using Spring Boot, you could also include the following in your application.yml:
info.release.version: ${version}
And the following in build.gradle:
processResources {
filesMatching('application.yml') {
expand(project.properties)
}
}
Lastly, you could also use the gradle-git-properties plugin, which is useful if you want to include the same project build information in response to GET /info (if you have the ‘info’ Spring Boot Actuator endpoint enabled, see the Spring Boot reference manual).
Read the version and tell Jenkins
Now that your build result has something on the filesystem containing the build version, you can extract it with a little Groovy code:
(That script assumes you are using the MANIFEST approach, see this gist for the Spring Boot/application.yml approach.)
Add this groovy script as a Build step, after your main build step:
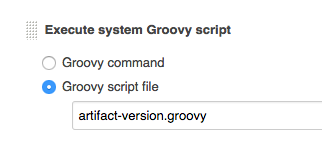
Tag and push
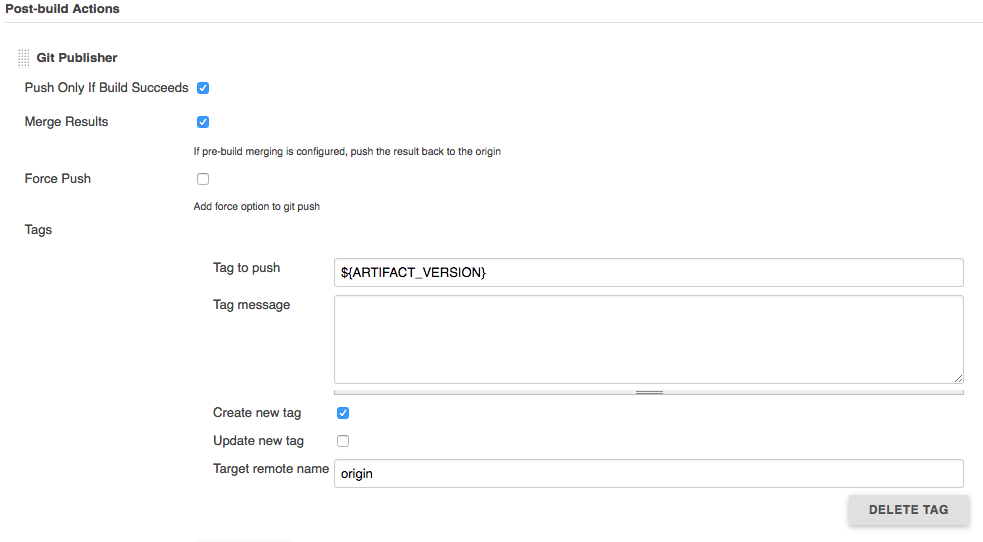
Last but not least we need to configure a post build step using the Git Plugin.
Under Post-build Actions, click Add Post Build Action, and select Git Publisher. In the Tags block, click Add tag. The Tag to push input should contain ${ARTIFACT_VERSION}, which is the environment variable we set by the groovy script.
Here’s a screenshot of the final configuration:
That’s it! Using this approach with Automating Release Management with Gradle and Jenkins results in all of your contributions being release-ready - without having to even consider publishing -SNAPSHOT builds.